|
A view of Byblos, Lebanon
 Lebanon (/ˈlɛbənɒn, -nən/ LEB-ə-non, -nən; Arabic: لُبْنَان, romanized: Lubnān, local pronunciation: [lɪbˈneːn]), officially the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in the Levant region of West Asia. It is bordered by Syria to the north and east, by Israel to the south, and by the Mediterranean Sea to the west; Cyprus lies a short distance away from the country's coastline. Lebanon is located at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian hinterlands. Lebanon has a population of more than five million people and covers an area of 10,452 square kilometres (4,036 sq mi). Beirut is the country's capital and largest city. The earliest evidence of human civilization in Lebanon dates back to 5000 BCE. From 3200 to 539 BC, what was to become Lebanon was part of Phoenicia, a maritime empire that stretched the Mediterranean Basin. In 64 BC, the region of Lebanon became part of the Roman Empire, which soon became a major center for Christianity under the aegis of the Byzantine Empire. After the 7th century, the region became under the rule of different caliphates, including the Rashidun, Umayyad and Abbasid caliphates. The 11th century saw the beginning of the Crusades and the establishment of Crusader states, which later fell to the Ayyubids and the Mamluks, and eventually to the Ottomans. Under Ottoman ruler Abdulmejid I, the first Lebanese proto-state was established in the form of the Mount Lebanon Mutasarrifate, created in the 19th century as a home for Maronite Christians under the Ottoman Tanzimat period. Lebanon is a developing country, ranked 112th on the Human Development Index. It has been classified as an upper-middle-income state. The Lebanese liquidity crisis, coupled with nationwide corruption and recent disasters such as the 2020 Beirut explosion, have precipitated the collapse of Lebanon's currency and fomented political instability, widespread resource shortages, and high unemployment and poverty. The World Bank has defined Lebanon's economic crisis as one of the world's worst since the 19th century. Despite the country's small size, Lebanese culture is renowned both in the Arab world and globally, powered primarily by the Lebanese diaspora. Lebanon is a founding member of the United Nations and of the Arab League, and is a member of the Non-Aligned Movement, the Organization of Islamic Cooperation, the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie, and the Group of 77, among others. (Full article...) This is a Featured article, one of the best articles Wikipedia has to offer.
Levantine Arabic, also called Shami (autonym: شامي šāmi or اللهجة الشامية el-lahje š-šāmiyye), is an Arabic variety spoken in the Levant, namely in Syria, Jordan, Lebanon, Palestine, Israel and southern Turkey (historically only in Adana, Mersin and Hatay provinces). With over 54 million speakers, Levantine is, alongside Egyptian, one of the two prestige varieties of spoken Arabic comprehensible all over the Arab world. Levantine is not officially recognized in any state or territory. Although it is the majority language in Jordan, Lebanon, Palestine, and Syria, it is predominantly used as a spoken vernacular in daily communication, whereas most written and official documents and media in these countries use the official Modern Standard Arabic (MSA), a form of literary Arabic only acquired through formal education that does not function as a native language. In Israel and Turkey, Levantine is a minority language. The Palestinian dialect is the closest vernacular Arabic variety to MSA, with about 50% of common words. Nevertheless, Levantine and MSA are not mutually intelligible. Levantine speakers therefore often call their language العامية al-ʿāmmiyya , 'slang', 'dialect', or 'colloquial'. However, with the emergence of social media, attitudes toward Levantine have improved. The amount of written Levantine has significantly increased, especially online, where Levantine is written using Arabic, Latin, or Hebrew characters. Levantine pronunciation varies greatly along social, ethnic, and geographical lines. Its grammar is similar to that shared by most vernacular varieties of Arabic. Its lexicon is overwhelmingly Arabic, with a significant Aramaic influence. (Full article...)
Religions in Lebanon Arab states Other countries This is a Good article, an article that meets a core set of editorial standards.
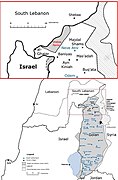
Hassan Ali "Soony" Saad (/ˈsuːni ˈsɑːd/ SOO-nee SAHD; Arabic: حسن علي "سوني" سعد, [ˈħasan ˈʕali ˈsoːni ˈsaʕad]; born August 17, 1992) is a professional footballer who plays as a forward for Malaysian club Penang and the Lebanon national team. Saad began his senior career with Major League Soccer (MLS) side Sporting Kansas City in 2011, with whom he won the 2012 U.S. Open Cup and 2013 MLS Cup. He moved to Thailand with BEC Tero Sasana before their 2015 season. However, due to an injury, he didn't appear for the club, and was sent out on loan to Pattaya United in the 2016 season. Saad returned to Sporting KC in 2017, and was sent on loan to their affiliate club Swope Park Rangers, before joining Indy Eleven in 2018. He then moved back to Asia, playing for Ansar in Lebanon, Ansan Greeners in South Korea, Al-Wehdat in Jordan, PT Prachuap in Thailand, and Penang in Malaysia. Born in the United States, Saad also holds Lebanese citizenship due to his origins. He is a former United States youth international and a full Lebanon international since 2013. Saad represented Lebanon at the 2023 AFC Asian Cup, the 2018 and 2022 FIFA World Cup qualifiers, the 2015 and 2019 AFC Asian Cup qualifiers, and the 2019 WAFF Championship. (Full article...)The following are images from various Lebanon-related articles on Wikipedia.
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Discover Wikipedia using portals |