Gondwana Rainforests: Difference between revisions
Reverted 1 edit by 2001:8003:44FB:1F00:D564:73E9:A60E:E4C3 (talk): Unconstructive. (TW) |
Salmoonlight (talk | contribs) Higher resolution image |
||
| (45 intermediate revisions by 32 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Area of subtropical rainforest in Australia}} |
|||
{{Use dmy dates|date=September 2014}} |
{{Use dmy dates|date=September 2014}} |
||
{{Use Australian English|date=September 2014}} |
{{Use Australian English|date=September 2014}} |
||
{{Infobox World Heritage Site |
{{Infobox UNESCO World Heritage Site |
||
| WHS = Gondwana Rainforests of Australia |
| WHS = Gondwana Rainforests of Australia<!-- leave empty, unless for stand-alone infoboxes that need a title different from the article title --> |
||
| |
| image = Box Log Falls, Springbrook National Park.jpg |
||
| image_upright = 1.2 |
|||
| imagecaption= Box Log Falls, [[Lamington National Park]] in [[Queensland]]. |
|||
| caption = Box Log Falls, [[Lamington National Park]] in [[Queensland]] |
|||
| State Party = Australia |
|||
| location = [[New South Wales]] and [[Queensland]], [[Australia]] |
|||
| Type = Natural |
|||
| includes = <!--replace by summary if the list of sub-entities is too large or incomplete--> |
|||
| Criteria = viii, ix, x |
|||
| criteria = {{UNESCO WHS type|(viii), (ix), (x)}}(viii), (ix), (x) |
|||
| ID = 368 |
|||
| ID = 368bis |
|||
| Region = [[List of World Heritage Sites in Asia and Australasia|Asia-Pacific]] |
|||
| coordinates = {{coord|28|15|S|150|3|E|display=inline, title|format=dms}} |
|||
| Year = 1986 |
|||
| |
| year = 1986 |
||
| extension = 1994 |
|||
| Link = http://whc.unesco.org/en/list/368 |
|||
| area = {{convert|370,000|ha|sqmi|abbr=on}} |
|||
| Extension = 1994 |
|||
| |
| embedded = {{Location map many | Australia |
||
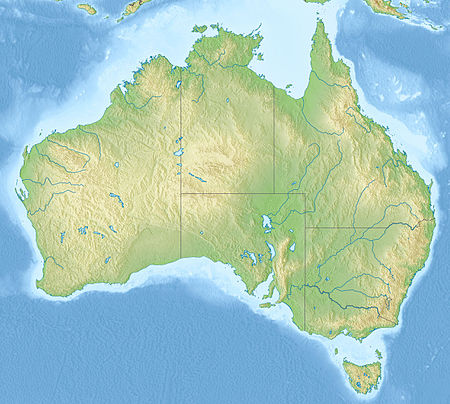
| caption = From the [[Main Range National Park|Main Range]] in the north to the [[Barrington Tops National Park|Barrington Tops]] in the south, various grouping of the Gondwana Rainforests on the Australian continent |
|||
| embedded = {{Location map many | Australia |
|||
| map_caption = From the [[Main Range National Park|Main Range]] in the north to the [[Barrington Tops National Park|Barrington Tops]] in the south, various grouping of the Gondwana Rainforests on the [[Australia]]n continent |
|||
| relief = 1 |
| relief = 1 |
||
| width = 300 |
| width = 300 |
||
| float = |
| float = none |
||
| border = none |
|||
| label1 = Acacia Plateau Flora Reserve (NSW) |
| label1 = Acacia Plateau Flora Reserve (NSW) |
||
| mark1size = 3 |
| mark1size = 3 |
||
| Line 243: | Line 244: | ||
| lon37_deg = 153 | lon37_min = 16 | lon37_dir=E |
| lon37_deg = 153 | lon37_min = 16 | lon37_dir=E |
||
}} |
}} |
||
{{Infobox designation list |
|||
| embed = yes |
|||
| designation1 = ANHL |
|||
| designation1_offname = ''Gondwana Rainforests of Australia'' |
|||
| designation1_type = National heritage (landscape) |
|||
| designation1_date = 17 December 1994 |
|||
| delisted1_date = |
|||
| designation1_partof = |
|||
| designation1_number = {{ANHL|105135}} |
|||
| designation1_free1name = Class |
|||
| designation1_free1value = Natural |
|||
| designation1_free2name = Legal Status |
|||
| designation1_free2value = Declared property |
|||
| designation1_free3name = List |
|||
| designation_free3value = [[World Heritage List]] |
|||
| designation2 = New South Wales State Heritage Register |
|||
| designation2_offname = ''Gondwana Rainforests of Australia''; ''Central Eastern Rainforest Reserves''; ''Gondwana Rainforests of Australia'' (new name from 2007); ''North East Rainforests World Heritage Area'' |
|||
| designation2_type = State heritage (landscape) |
|||
| designation2_date = 2 April 1999 |
|||
| delisted2_date = |
|||
| designation2_partof = |
|||
| designation2_number = 1002 |
|||
| designation2_free1name = Type |
|||
| designation2_free1value = Wilderness |
|||
| designation2_free2name = Category |
|||
| designation2_free2value = Landscape – Natural |
|||
| designation2_free3name = Builders |
|||
| designation2_free3value = |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
}} |
|||
The '''Gondwana Rainforests''' of [[Australia]], formerly known as the '''Central Eastern Rainforest Reserves''', are the most extensive area of subtropical [[rainforest]] in the world.<ref name="ausgovdep">{{cite web |url=http://www.environment.gov.au/heritage/places/world/gondwana/index.html |title=Gondwana Rainforests of Australia |accessdate=31 August 2008|date= |work=[[Department of the Environment (Australia)|Department of the Environment]]|publisher=[[Australian Government]] }}</ref> Collectively, the rainforests are a [[World Heritage Site]] with fifty separate reserves totalling {{convert|366500|ha|acre}} from {{NSWcity|Newcastle}} to [[Brisbane]].<ref name="explore">{{cite book |title=Australia's National and Marine Parks: Queensland |last=Reid |first=Greg |authorlink= |coauthors= |year=2004 |publisher=Macmillan Education Australia |location=South Yarra, Victoria|isbn=0-7329-9053-X |page=11 }}</ref> |
|||
The '''Gondwana Rainforests''' of [[Australia]], formerly known as the '''Central Eastern Rainforest Reserves''', are the most extensive area of subtropical [[rainforest]] in the world.<ref name="ausgovdep">{{cite web |url=http://www.environment.gov.au/heritage/places/world/gondwana/index.html |title=Gondwana Rainforests of Australia |access-date=31 August 2008 |work=[[Department of the Environment (Australia)|Department of the Environment]] |publisher=[[Australian Government]] |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080726061553/http://www.environment.gov.au/heritage/places/world/gondwana/index.html |archive-date=26 July 2008 |df=dmy-all }}</ref> Collectively, the rainforests are a [[World Heritage Site]] with fifty separate reserves totalling {{convert|366500|ha|acre}} from {{NSWcity|Newcastle}} to [[Brisbane]].<ref name="explore">{{cite book |title=Australia's National and Marine Parks: Queensland |last=Reid |first=Greg |year=2004 |publisher=Macmillan Education Australia |location=South Yarra, Victoria|isbn=0-7329-9053-X |page=11 }}</ref> |
|||
==Background== |
|||
The Gondwana Rainforests are so-named because the [[fossil]] record indicates that when [[Gondwana]] existed it was covered by rainforests containing the same kinds of species that are living today. Not all Gondwanan rainforests in Australia are located in the New South Wales{{spaced endash}}Queensland region; the largest Gondwanan rainforest in Australia is located in Tasmania's [[Tarkine wilderness]]. The number of visitors to the Gondwana rainforest reserves in New South Wales and Queensland is about 2 million per year.<ref name="ausgovdep" /> |
|||
The Gondwana Rainforests are so-named because the [[fossil]] record indicates that when [[Gondwana]] existed it was covered by rainforests containing the same kinds of species that are living today. Not all Gondwanan rainforests in Australia are located in the [[New South Wales]]{{spaced endash}}[[Queensland]] region; the largest Gondwanan rainforest in Australia is located in [[Tasmania|Tasmania's]] [[Tarkine wilderness]]. The number of visitors to the Gondwana rainforest reserves in New South Wales and Queensland is about 2 million per year.<ref name="ausgovdep" /> |
|||
The World Heritage status of the region was created and negotiated initially in 1986, with the area extended in 1994, |
The World Heritage status of the region was created and negotiated initially in 1986, with the area extended in 1994, following a nomination which was prepared in 1992 by the Rainforest Conservation Society.<ref>{{Citation|author1=Keto, Aila | author-link1=Aila Keto | author2=Scott, Keith | title=The central eastern rainforests of Australia : World Heritage nomination | publication-date=1992 | publisher=Rainforest Conservation Society | url=https://trove.nla.gov.au/work/24045583 | access-date=14 October 2021 | archive-date=27 October 2021 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211027183844/https://trove.nla.gov.au/work/24045583 | url-status=live }}</ref> The World Heritage listing carries the following inscription:<ref name="ausgovdep" /> |
||
{{quotation| |
{{quotation|The Gondwana Rainforests of Australia is a serial property comprising the major remaining areas of rainforest in southeast Queensland and northeast New South Wales. It represents outstanding examples of major stages of the Earth’s evolutionary history, ongoing geological and biological processes, and exceptional biological diversity. A wide range of plant and animal lineages and communities with ancient origins in Gondwana, many of which are restricted largely or entirely to the Gondwana Rainforests, survive in this collection of reserves. The Gondwana Rainforests also provides the principal habitat for many threatened species of plants and animals.|Brief synthesis of the Gondwana Rainforests of Australia as inscribed on the [[UNESCO]] [[World Heritage Site|World Heritage List]].}} |
||
The site was [[government gazette|gazetted]] on the [[Australian National Heritage List]] on 21 May 2007<ref name=anhl>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.gov.au/cgi-bin/ahdb/search.pl?mode=place_detail;place_id=105135|title=Gondwana Rainforests of Australia, Lismore, NSW, Australia|work=Australian Heritage Database: [[Department of the Environment (Australia)|Department of the Environment]]|date=2014| |
The site was [[government gazette|gazetted]] on the [[Australian National Heritage List]] on 21 May 2007<ref name=anhl>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.gov.au/cgi-bin/ahdb/search.pl?mode=place_detail;place_id=105135|title=Gondwana Rainforests of Australia, Lismore, NSW, Australia|work=Australian Heritage Database: [[Department of the Environment (Australia)|Department of the Environment]]|date=2014|access-date=7 September 2014|publisher=[[Australian Government]]|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140510073429/http://www.environment.gov.au/cgi-bin/ahdb/search.pl?mode=place_detail;place_id=105135|archive-date=10 May 2014|url-status=live}}</ref> under the {{Cite Legislation AU|Cth|act|eahlaa12003459|Environment and Heritage Legislation Amendment Act (No. 1), 2003}};<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.gov.au/system/files/pages/758ea283-6b9d-41bc-a29a-1276e1c7fced/files/10568601.pdf|type=PDF|title=Determination regarding including World Heritage places in the National Heritage List|work=[[Government gazette|Special government gazette]]|number=S.99|date=21 May 2007|access-date=30 August 2014|publisher=[[Department of the Environment (Australia)|Department of the Environment and Water Resources]], [[Commonwealth of Australia]]|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140903135629/http://www.environment.gov.au/system/files/pages/758ea283-6b9d-41bc-a29a-1276e1c7fced/files/10568601.pdf|archive-date=3 September 2014|df=dmy-all}}</ref> and the New South Wales portion was added to the [[New South Wales State Heritage Register]] on 2 April 1999.<ref name=nswshr-1002>{{cite NSW SHR|5014148|Gondwana Rainforests of Australia|hr=01002|fn=H99/00224/5|access-date=2 June 2018}}</ref> |
||
== Conservation value == |
== Conservation value == |
||
The forests were inscribed to the World Heritage list in 1986, covering only the New South Wales sites of approximately {{convert|310800|ha}} and extended in 1994 to cover the Queensland sites of approximately {{convert|59200|ha}} which is a total of approximately {{convert|370000|ha}}. The rainforest reserves have an extremely high conservation value, with more than 200 rare or threatened plant and animal species.<ref name="explore" /> |
The forests were inscribed to the World Heritage list in 1986, covering only the New South Wales sites of approximately {{convert|310800|ha}} and extended in 1994 to cover the Queensland sites of approximately {{convert|59200|ha}} which is a total of approximately {{convert|370000|ha}}. The rainforest reserves have an extremely high conservation value, with more than 200 rare or threatened plant and animal species.<ref name="explore" /> |
||
Eight separate areas have been identified as having outstanding heritage significance to Australia and are included on the [[Australian National Heritage List]].<ref name=anhl/> The altitude of the reserves ranges from sea level to almost {{convert|1600|m|ft|abbr=on}}.<ref name="eos">{{cite web |url=http://www.eoearth.org/article/Central_Eastern_Rainforest_Reserves,_Australia#Physical_Features |title=Central Eastern Rainforest Reserves, Australia |author=McGinley, Mark| |
Eight separate areas have been identified as having outstanding heritage significance to Australia and are included on the [[Australian National Heritage List]].<ref name=anhl/> The altitude of the reserves ranges from sea level to almost {{convert|1600|m|ft|abbr=on}}.<ref name="eos">{{cite web |url=http://www.eoearth.org/article/Central_Eastern_Rainforest_Reserves,_Australia#Physical_Features |title=Central Eastern Rainforest Reserves, Australia |author=McGinley, Mark |access-date=1 July 2009 |date=9 December 2008 |work=[[Encyclopedia of Earth]] |publisher=United Nations Environment Programme: World Conservation Monitoring Centre |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091016064413/http://www.eoearth.org/article/Central_Eastern_Rainforest_Reserves%2C_Australia#Physical_Features |archive-date=16 October 2009 |df=dmy-all }}</ref> |
||
On 22 December 2000, the [[High Conservation Value Old Growth forest]] covering 24 national parks and 19 nature reserves spread across 12 [[Local government in New South Wales|local government areas]] in the upper north east region of New South Wales were listed on the [[New South Wales State Heritage Register]].<ref name=nswshr-1487>{{cite NSW SHR|5051503|High Conservation Value Old Growth forest|hr=01487|fn=H99/00224; EF14/5007|access-date=18 May 2018}}</ref> |
|||
==National Parks== |
|||
==National parks== |
|||
The Queensland areas include the [[Main Range National Park|Main Range]], at its most northern point; and extending south, the [[Lamington National Park|Lamington]], [[Mount Chinghee National Park|Mount Chinghee]], [[Springbrook National Park|Springbrook ]] and [[Mount Barney National Park|Mount Barney]] national parks. |
The Queensland areas include the [[Main Range National Park|Main Range]], at its most northern point; and extending south, the [[Lamington National Park|Lamington]], [[Mount Chinghee National Park|Mount Chinghee]], [[Springbrook National Park|Springbrook ]] and [[Mount Barney National Park|Mount Barney]] national parks. |
||
The New South Wales areas include the [[Barrington Tops National Park|Barrington Tops]], at its most southern point; and extending north, the [[Dorrigo National Park|Dorrigo]], [[Mount Warning National Park|Mount Warning]], [[New England National Park|New England]], [[Mebbin National Park|Mebbin]], [[Nightcap National Park|Nightcap]], [[Border Ranges National Park|Border Ranges]], [[Oxley Wild Rivers National Park|Oxley Wild Rivers]], [[Washpool National Park|Washpool]], [[Willi Willi National Park|Willi Willi]] and [[Werrikimbe National Park|Werrikimbe]] national parks.<ref>{{cite web |
The New South Wales areas include the [[Barrington Tops National Park|Barrington Tops]], at its most southern point; and extending north, the [[Dorrigo National Park|Dorrigo]], [[Mount Warning National Park|Mount Warning]], [[New England National Park|New England]], [[Mebbin National Park|Mebbin]], [[Nightcap National Park|Nightcap]], [[Border Ranges National Park|Border Ranges]], [[Oxley Wild Rivers National Park|Oxley Wild Rivers]], [[Washpool National Park|Washpool]], [[Willi Willi National Park|Willi Willi]] and [[Werrikimbe National Park|Werrikimbe]] national parks.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/368/multiple=1&unique_number=422|title=Gondwana Rainforests of Australia|access-date=9 June 2008|work=World Heritage List|publisher=[[UNESCO]]|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080527051520/https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/368/multiple%3D1%26unique_number%3D422|archive-date=27 May 2008|df=dmy-all}}</ref> |
||
The most heavily visited parts are Dorrigo National Park and the Natural Bridge section of Springbrook National Park.<ref name="eos"/> |
The most heavily visited parts are Dorrigo National Park and the Natural Bridge section of Springbrook National Park.<ref name="eos"/> |
||
== Destruction == |
|||
The region was historically [[Logging|logged]] extremely heavily, to such an extent that only 1% of the original range of the Gondwana rainforest remains in Australia. Most of the logged regions have been taken over by [[eucalyptus]] forest. <ref name=":0">{{Cite web|url=https://www.abc.net.au/news/2020-01-18/gondwana-era-nightcap-oak-devastated-by-bushfire/11877770|title=Gondwana-era nightcap oak devastated by unprecedented bushfire|last=Shoebridge|first=Joanne|last2=Marciniak|first2=Catherine|date=2020-01-18|website=[[ABC News (Australia)]]|access-date=2020-01-18|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200118025250/https://www.abc.net.au/news/2020-01-18/gondwana-era-nightcap-oak-devastated-by-bushfire/11877770|archive-date=18 January 2020|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
During the [[2019–20 Australian bushfire season|2019-2020 Australian bushfire season]], many regions of the Gondwana rainforest were devastated by [[Bushfires in Australia|bushfires]] for the first time, with some preliminary reports indicating that up to 53% of the forests may have burned as of January 2020. Among the devastated habitats are several locations that are significant for some critically imperiled species, such as the [[Eidothea hardeniana|nightcap oak]] and the [[giant barred frog]]. The presence of these devastating blazes in areas that have never burned before has been linked to the encroachment of the flammable eucalyptus trees into the logged areas adjoining the forests.<ref name=":0" /><ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2020/jan/17/its-heart-wrenching-80-of-blue-mountains-and-50-of-gondwana-rainforests-burn-in-bushfires|title='It's heart-wrenching': 80% of Blue Mountains and 50% of Gondwana rainforests burn in bushfires|last=Cox|first=Lisa|date=2020-01-16|work=[[The Guardian]]|access-date=2020-01-18|last2=Evershed|first2=Nick|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200118234106/https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2020/jan/17/its-heart-wrenching-80-of-blue-mountains-and-50-of-gondwana-rainforests-burn-in-bushfires|archive-date=18 January 2020|url-status=live}}</ref> The general claim of "never burned before" has been challenged by several commentators, based on an article in ''[[The Cairns Post]]'' on 25 October 1951 that reported a "fire has burnt out about 2000 acres of thick rainforest country" in the Lamington National Park.<ref>{{cite news|url=https://trove.nla.gov.au/newspaper/article/42728679|title=Bushfires Over Large Part of State|newspaper=[[The Cairns Post]]|date=25 October 1951|page=1|via=[[Trove]]}}</ref> |
|||
==Australian National Heritage List sections== |
==Australian National Heritage List sections== |
||
| Line 282: | Line 320: | ||
! scope="col" | sq mi |
! scope="col" | sq mi |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| scope="row" rowspan="10" | '''Main Range''' group;<br />near [[Killarney, Queensland|Killarney]] |
| scope="row" rowspan="10" | '''Main Range''' group;<br />near [[Killarney, Queensland|Killarney]] |
||
| Acacia Plateau Flora Reserve |
| Acacia Plateau Flora Reserve |
||
| [[New South Wales|NSW]] |
| [[New South Wales|NSW]] |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Emu Vale State Forest (part) |
| Emu Vale State Forest (part) |
||
| [[Queensland|Qld]] |
| [[Queensland|Qld]] |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Gambubal State Forest (part) |
| Gambubal State Forest (part) |
||
| Qld |
| Qld |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Line 307: | Line 345: | ||
| Qld |
| Qld |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Goomburra State Forest (part) |
| Goomburra State Forest (part) |
||
| Qld |
| Qld |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Main Range National Park]] |
| [[Main Range National Park]] |
||
| Qld |
| Qld |
||
| [[File:Queen Mary Falls3.jpg|100px]] |
| [[File:Queen Mary Falls3.jpg|100px]] |
||
| {{convert|184|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
| {{convert|184|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
||
| {{coord|27|48|57|S|152|15|56|E|display=inline}} |
| {{coord|27|48|57|S|152|15|56|E|display=inline}} |
||
|<ref name=mr>{{cite web|url=http://www.nprsr.qld.gov.au/managing/plans-strategies/statements/main-range.html|title=Main Range National Park and Spicers Gap Road Regional Park Management Statement 2013|work=Department of National Parks, Recreation, Sport and Racing|publisher=[[Government of Queensland]]|date=11 November 2013| |
|<ref name=mr>{{cite web|url=http://www.nprsr.qld.gov.au/managing/plans-strategies/statements/main-range.html|title=Main Range National Park and Spicers Gap Road Regional Park Management Statement 2013|work=Department of National Parks, Recreation, Sport and Racing|publisher=[[Government of Queensland]]|date=11 November 2013|access-date=7 September 2014|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140908155007/http://www.nprsr.qld.gov.au/managing/plans-strategies/statements/main-range.html|archive-date=8 September 2014|df=dmy-all}}</ref> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Spicers Gap Road Conservation Park]] |
| [[Spicers Gap Road Conservation Park]] |
||
| Qld |
| Qld |
||
| [[File:Moss's Well.jpg|100px]] |
| [[File:Moss's Well.jpg|100px]] |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| {{coord|28|04|35|S|152|23|26|E|display=inline}} |
| {{coord|28|04|35|S|152|23|26|E|display=inline}} |
||
|<ref name=mr/> |
|<ref name=mr/> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Spicers Gap State Forest (part) |
| Spicers Gap State Forest (part) |
||
| Qld |
| Qld |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Line 343: | Line 381: | ||
| Qld |
| Qld |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Line 350: | Line 388: | ||
| NSW |
| NSW |
||
| [[File:Wilsons Peak-1995 Dec.jpg|100px]] |
| [[File:Wilsons Peak-1995 Dec.jpg|100px]] |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| {{coord|28|15|19|S|152|29|21|E|display=inline}} |
| {{coord|28|15|19|S|152|29|21|E|display=inline}} |
||
|<ref>{{ |
|<ref name="hunter 2004">{{citation |mode=cs1 |url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/resources/parks/cerra-values-report.pdf#75 |format=PDF |section=9.2 Main Range Group |title=World Heritage and Associative Natural Values of the Central Eastern Rainforest Reserves of Australia |publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]] |orig-year=June 2003 |date=December 2004 |access-date=22 September 2014 |last=Hunter |first=R. John |page=66 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150924070344/http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/resources/parks/cerra-values-report.pdf#75 |archive-date=24 September 2015}}</ref> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| scope="row" rowspan="7" | '''Focal Peak''' group;<br />on the |
| scope="row" rowspan="7" | '''Focal Peak''' group;<br />on the NSW–Qld border |
||
| Burnett Creek State Forest (part) |
| Burnett Creek State Forest (part) |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Captains Creek Flora Reserve (part) |
| Captains Creek Flora Reserve (part) |
||
| |
|||
| |
|||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
|||
| |
|||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Mallanganee National Park]] |
| [[Mallanganee National Park]] |
||
| NSW |
| NSW |
||
| |
| |
||
| {{convert|11|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
| {{convert|11|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
||
| {{coord|25|55|09|S|152|45|13|E|display=inline}} |
| {{coord|25|55|09|S|152|45|13|E|display=inline}} |
||
|<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkHome.aspx?id=N0142|title=Mallanganee National Park|work=Office of Environment and Heritage|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|date=| |
|<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkHome.aspx?id=N0142|title=Mallanganee National Park|work=Office of Environment and Heritage|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|access-date=7 September 2014|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140907171232/http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkHome.aspx?id=N0142|archive-date=7 September 2014|df=dmy-all}}</ref> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Mount Clunie National Park]] (part) |
| [[Mount Clunie National Park]] (part) |
||
| NSW |
| NSW |
||
| |
| |
||
| {{convert|14|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
| {{convert|14|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
||
| {{coord|28|19|27|S|152|31|12|E|display=inline}} |
| {{coord|28|19|27|S|152|31|12|E|display=inline}} |
||
|<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkHome.aspx?id=N0146|title=Mount Clunie National Park|work=Office of Environment and Heritage|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|date=| |
|<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkHome.aspx?id=N0146|title=Mount Clunie National Park|work=Office of Environment and Heritage|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|access-date=10 September 2014|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140911002413/http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkHome.aspx?id=N0146|archive-date=11 September 2014|df=dmy-all}}</ref> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Mount Nothofagus National Park]] (part) |
| [[Mount Nothofagus National Park]] (part) |
||
| NSW |
| NSW |
||
| |
| |
||
| {{convert|22|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
| {{convert|22|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
||
| {{coord|28|19|02|S|152|38|01|E|display=inline}} |
| {{coord|28|19|02|S|152|38|01|E|display=inline}} |
||
|<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkHome.aspx?id=N0147|title=Mount Nothofagus National Park|work=Office of Environment and Heritage|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|date=| |
|<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkHome.aspx?id=N0147|title=Mount Nothofagus National Park|work=Office of Environment and Heritage|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|access-date=10 September 2014|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140911001701/http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkHome.aspx?id=N0147|archive-date=11 September 2014|df=dmy-all}}</ref> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Tooloom National Park]] (part) |
| [[Tooloom National Park]] (part) |
||
| NSW |
| NSW |
||
| [[File:White Beech - Tooloom.jpg|100px]] |
| [[File:White Beech - Tooloom.jpg|100px]] |
||
| {{convert|44|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
| {{convert|44|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
||
| {{coord|28|26|47|S|152|27|13|E|display=inline}} |
| {{coord|28|26|47|S|152|27|13|E|display=inline}} |
||
|<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkManagement.aspx?id=N0091|title=Tooloom National Park: Park management|work=Office of Environment and Heritage|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|date=| |
|<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkManagement.aspx?id=N0091|title=Tooloom National Park: Park management|work=Office of Environment and Heritage|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|access-date=10 September 2014|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140910195814/http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkManagement.aspx?id=N0091|archive-date=10 September 2014|df=dmy-all}}</ref> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Toonumbar National Park]] (part) |
| [[Toonumbar National Park]] (part) |
||
| NSW |
| NSW |
||
| [[File:Toonumbar National Park Murray Scrub January 1995.jpg|100px]] |
| [[File:Toonumbar National Park Murray Scrub January 1995.jpg|100px]] |
||
| {{convert|149|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
| {{convert|149|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
||
| {{coord|28|29|16|S|152|43|33|E|display=inline}} |
| {{coord|28|29|16|S|152|43|33|E|display=inline}} |
||
|<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkHome.aspx?id=N0092|title=Toonumbar National Park|work=Office of Environment and Heritage|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|date=| |
|<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkHome.aspx?id=N0092|title=Toonumbar National Park|work=Office of Environment and Heritage|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|access-date=10 September 2014|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140911001914/http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkHome.aspx?id=N0092|archive-date=11 September 2014|df=dmy-all}}</ref> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| scope="row" rowspan=" |
| scope="row" rowspan="11" | '''Shield Volcano''' group;<br />on the NSW–Qld border<br />on the [[McPherson Range|McPherson]] and [[Tweed Range|Tweed]] ranges |
||
| Amaroo Flora Reserve |
| Amaroo Flora Reserve |
||
| |
|||
| |
|||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
|||
| |
|||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Border Ranges National Park]] (part) |
| [[Border Ranges National Park]] (part) |
||
| NSW |
| NSW |
||
| [[File:Brindle Creek Border Ranges National Park.jpg|100px]] |
| [[File:Brindle Creek Border Ranges National Park.jpg|100px]] |
||
| {{convert|317|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
| {{convert|317|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
||
| {{coord|28|21|35|S|152|59|10|E|display=inline}} |
| {{coord|28|21|35|S|152|59|10|E|display=inline}} |
||
|<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkManagement.aspx?id=N0050|title=Border Ranges National Park: Park management|work=[[National Parks and Wildlife Service (New South Wales)|NSW National Parks & Wildlife Service]]|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|date=| |
|<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkManagement.aspx?id=N0050|title=Border Ranges National Park: Park management|work=[[National Parks and Wildlife Service (New South Wales)|NSW National Parks & Wildlife Service]]|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140911001658/http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkManagement.aspx?id=N0050|archive-date=11 September 2014|df=dmy-all}}</ref> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Lamington National Park]] |
| [[Lamington National Park]] |
||
| Qld |
| Qld |
||
| [[File:Ships Stern Lamington National Park.jpg|100px]] |
| [[File:Ships Stern Lamington National Park.jpg|100px]] |
||
| Line 427: | Line 465: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Limpinwood Nature Reserve]] |
| [[Limpinwood Nature Reserve]] |
||
| NSW |
| NSW |
||
| |
| |
||
| {{convert|26.5|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
| {{convert|26.5|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
||
| {{coord|28|17|56|S|153|10|26|E|display=inline}} |
| {{coord|28|17|56|S|153|10|26|E|display=inline}} |
||
|<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkHome.aspx?id=N0444|title=Limpinwood Nature Reserve: Park management|work=Office of Environment and Heritage|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|date |
|<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkHome.aspx?id=N0444|title=Limpinwood Nature Reserve: Park management|work=Office of Environment and Heritage|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|access-date=28 September 2014|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141205032620/http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkHome.aspx?id=N0444|archive-date=5 December 2014|df=dmy-all}}</ref> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Mebbin National Park]] (part) |
| [[Mebbin National Park]] (part) |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
|||
| |
|||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|||
| [[Mount Chinghee National Park]] |
|||
| |
| |
||
| [[File:Mount Chinghee at Running Creek, Queensland.jpg|100px]] |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Mount |
| [[Mount Chinghee National Park]] |
||
| |
|||
| [[File:Mount Chinghee at Running Creek, Queensland.jpg|100px]] |
|||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
|||
| |
|||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Nightcap National Park]] (part) |
| [[Nightcap National Park]] (part) |
||
| |
|||
| |
|||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
|||
| |
|||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Numinbah Nature Reserve]] |
| [[Numinbah Nature Reserve]] |
||
| NSW |
| NSW |
||
| [[File:habitat of Endiandra globosa and E floydii - NSW Qld border.jpg|100px]] |
| [[File:habitat of Endiandra globosa and E floydii - NSW Qld border.jpg|100px]] |
||
| {{convert|8.6|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
| {{convert|8.6|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
||
| {{coord|28|15||S|153|16||E|display=inline}} |
| {{coord|28|15||S|153|16||E|display=inline}} |
||
|<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkManagement.aspx?id=N0545|title=Numinbah Nature Reserve: Park management|work=Office of Environment and Heritage|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|date=| |
|<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkManagement.aspx?id=N0545|title=Numinbah Nature Reserve: Park management|work=Office of Environment and Heritage|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|access-date=28 September 2014|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140913053735/http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkManagement.aspx?id=N0545|archive-date=13 September 2014|df=dmy-all}}</ref> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Springbrook National Park]] (part) |
| [[Springbrook National Park]] (part) |
||
| Qld |
| Qld |
||
| [[File:IMAG0310.jpg|100px]] |
| [[File:IMAG0310.jpg|100px]] |
||
| {{convert|62|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
| {{convert|62|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
||
| {{coord|28|08|24|S|153|16|27|E|display=inline}} |
| {{coord|28|08|24|S|153|16|27|E|display=inline}} |
||
|<ref name="epa1">{{cite web|url=http://www.derm.qld.gov.au/parks/springbrook/culture.html|title=Springbrook National Park: Nature, culture and history| |
|<ref name="epa1">{{cite web|url=http://www.derm.qld.gov.au/parks/springbrook/culture.html|title=Springbrook National Park: Nature, culture and history|access-date=12 July 2009|date=29 April 2009|publisher=[[Government of Queensland]]|work=Department of Environment, Resources, and Mining|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100324204205/http://www.derm.qld.gov.au/parks/springbrook/culture.html|archive-date=24 March 2010|df=dmy-all}}</ref> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| various Rabbit Board Reserves<br />along the [[ |
| various Rabbit Board Reserves<br />along the [[Darling Downs-Moreton Rabbit Board fence|Rabbit Board fence]] |
||
| |
|||
| |
|||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
|||
| |
|||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Wollumbin National Park]] |
| [[Wollumbin National Park]] |
||
| NSW |
| NSW |
||
| [[File:AU Mt Warning from Tweed.jpg|100px]] |
| [[File:AU Mt Warning from Tweed.jpg|100px]] |
||
| {{convert|24|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
| {{convert|24|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
||
| {{coord|28|23|23|S|153|16|7|E|display=inline}} |
| {{coord|28|23|23|S|153|16|7|E|display=inline}} |
||
|<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkHome.aspx?id=N0183|title=Wollumbin National Park|work=[[National Parks and Wildlife Service (New South Wales)|NSW National Parks & Wildlife Service]]|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|date=24 September 2013| |
|<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkHome.aspx?id=N0183|title=Wollumbin National Park|work=[[National Parks and Wildlife Service (New South Wales)|NSW National Parks & Wildlife Service]]|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|date=24 September 2013|access-date=1 May 2014|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140502002313/http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkHome.aspx?id=N0183|archive-date=2 May 2014|df=dmy-all}}</ref> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| scope="row" | '''Coastal''' group;<br />on the coast at [[Iluka, New South Wales|Iluka]] |
| scope="row" | '''Coastal''' group;<br />on the coast at [[Iluka, New South Wales|Iluka]] |
||
| Line 496: | Line 527: | ||
| {{convert|1.35|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
| {{convert|1.35|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
||
| {{coord|29|24|14|S|153|21|44|E|display=inline}} |
| {{coord|29|24|14|S|153|21|44|E|display=inline}} |
||
|<ref>{{cite web|title=Iluka Nature Reserve: Park management|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkManagement.aspx?id=N0510|work=Office of Environment and Heritage|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|date |
|<ref>{{cite web|title=Iluka Nature Reserve: Park management|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkManagement.aspx?id=N0510|work=Office of Environment and Heritage|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|access-date=23 September 2014|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141011003818/http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkManagement.aspx?id=N0510|archive-date=11 October 2014|df=dmy-all}}</ref> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| scope="row" rowspan="2" | '''Washpool and Gibraltar Range''' group;<br />[[contiguous]] areas between [[Glen Innes, New South Wales|Glen Innes]] and [[Grafton, New South Wales|Grafton]] |
| scope="row" rowspan="2" | '''Washpool and Gibraltar Range''' group;<br />[[Geographic contiguity|contiguous]] areas between [[Glen Innes, New South Wales|Glen Innes]] and [[Grafton, New South Wales|Grafton]] |
||
| [[Gibraltar Range National Park]] |
| [[Gibraltar Range National Park]] |
||
| NSW |
| NSW |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Line 509: | Line 540: | ||
| NSW |
| NSW |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Line 517: | Line 548: | ||
| NSW |
| NSW |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Dorrigo National Park]] (part) |
| [[Dorrigo National Park]] (part) |
||
| NSW |
| NSW |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Mount Hyland Nature Reserve]] (part) |
| [[Mount Hyland Nature Reserve]] (part) |
||
| NSW |
| NSW |
||
| [[File:Mount Hyland Nature Reserve Dec 31 1994.jpg|100px]] |
| [[File:Mount Hyland Nature Reserve Dec 31 1994.jpg|100px]] |
||
| {{convert|25|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
| {{convert|25|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
||
| {{coord|30|9|36|S|152|26|42|E|display=inline}} |
| {{coord|30|9|36|S|152|26|42|E|display=inline}} |
||
|<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkManagement.aspx?id=N0566|title=Mount Hyland Nature Reserve: Park management|work=Office of Environment and Heritage|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|date |
|<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkManagement.aspx?id=N0566|title=Mount Hyland Nature Reserve: Park management|work=Office of Environment and Heritage|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|access-date=28 September 2014|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141205031726/http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkManagement.aspx?id=N0566|archive-date=5 December 2014|df=dmy-all}}</ref> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[New England National Park]] (part) |
| [[New England National Park]] (part) |
||
| NSW |
| NSW |
||
| [[File:N Eng NP (1).jpg|100px]] |
| [[File:N Eng NP (1).jpg|100px]] |
||
| {{convert|673|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
| {{convert|673|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
||
| {{coord|30|35|34|S|152|27|30|E|display=inline}} |
| {{coord|30|35|34|S|152|27|30|E|display=inline}} |
||
|<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkManagement.aspx?id=N0028|title=New England National Park: Park management|work=Office of Environment and Heritage|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|date=| |
|<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkManagement.aspx?id=N0028|title=New England National Park: Park management|work=Office of Environment and Heritage|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|access-date=10 September 2014|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140911001917/http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkManagement.aspx?id=N0028|archive-date=11 September 2014|df=dmy-all}}</ref> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| scope="row" rowspan="6" | '''Hastings{{endash}}Macleay''' group;<br />southeast of [[ |
| scope="row" rowspan="6" | '''Hastings{{endash}}Macleay''' group;<br />southeast of [[Armidale]] |
||
| [[Fenwicks Scrub Flora Reserve]] |
| [[Fenwicks Scrub Flora Reserve]] |
||
| NSW |
| NSW |
||
| Line 548: | Line 579: | ||
| {{convert|1.1|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
| {{convert|1.1|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
||
| {{coord|31|17||S|152|8.8||E|display=inline}} |
| {{coord|31|17||S|152|8.8||E|display=inline}} |
||
|<ref name="hunter 2004" /> |
|||
|<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/resources/parks/cerra-values-report.pdf#104|type=PDF|section=9.8 Hastings Group|title=World Heritage and Associative Natural Values of the Central Eastern Rainforest Reserves of Australia|work=[[National Parks and Wildlife Service (New South Wales)|NSW National Parks & Wildlife Service]]|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|origyear=June 2003 |date=December 2004|accessdate=20 September 2014|author=Hunter, R. John|page=95}}</ref> |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| Mount Seaview Nature Reserve |
| Mount Seaview Nature Reserve |
||
| NSW |
| NSW |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Oxley Wild Rivers National Park]] (part) |
| [[Oxley Wild Rivers National Park]] (part) |
||
| NSW |
| NSW |
||
| [[File:ParadiseRocks.jpg|100px]] |
| [[File:ParadiseRocks.jpg|100px]] |
||
| {{convert|1452|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
| {{convert|1452|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
||
| {{coord|30|59|47|S|152|00|36|E|display=inline}} |
| {{coord|30|59|47|S|152|00|36|E|display=inline}} |
||
|<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkManagement.aspx?id=N0043|title=Oxley Wild Rivers National Park: Park Management|work=Office of Environment and Heritage|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|date=| |
|<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkManagement.aspx?id=N0043|title=Oxley Wild Rivers National Park: Park Management|work=Office of Environment and Heritage|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|access-date=10 September 2014|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140911002518/http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkManagement.aspx?id=N0043|archive-date=11 September 2014|df=dmy-all}}</ref> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| The Castles Flora Reserve |
| The Castles Flora Reserve |
||
| NSW |
| NSW |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| {{coord|30|59|55|S|152|20|5|E|display=inline}} |
| {{coord|30|59|55|S|152|20|5|E|display=inline}} |
||
|<ref>{{Gazetteer of Australia|name=The Castles Flora Reserve (NSW)|feature=NSW72143}}</ref> |
|<ref>{{Gazetteer of Australia|name=The Castles Flora Reserve (NSW)|feature=NSW72143}}</ref> |
||
| Line 576: | Line 607: | ||
| [[File:Werrikimbe.jpg|100px]] |
| [[File:Werrikimbe.jpg|100px]] |
||
| {{convert|333|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
| {{convert|333|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
||
| {{coord|31|12||S|152|14||E|display=inline}} |
| {{coord|31|12||S|152|14||E|display=inline}} |
||
|<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkHome.aspx?id=N0042|title=Werrikimbe National Park|work=Office of Environment and Heritage|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|date=| |
|<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkHome.aspx?id=N0042|title=Werrikimbe National Park|work=Office of Environment and Heritage|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|access-date=10 September 2014|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140912135903/http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkHome.aspx?id=N0042|archive-date=12 September 2014|df=dmy-all}}</ref> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Willi Willi National Park]] (part) |
| [[Willi Willi National Park]] (part) |
||
| NSW |
| NSW |
||
| |
| |
||
| {{convert|299|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
| {{convert|299|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
||
| {{coord|31|10|43|S|152|29|27|E|display=inline}} |
| {{coord|31|10|43|S|152|29|27|E|display=inline}} |
||
|<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkManagement.aspx?id=N0102|title=Willi Willi National Park|work=Office of Environment and Heritage|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|date |
|<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkManagement.aspx?id=N0102|title=Willi Willi National Park|work=Office of Environment and Heritage|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|access-date=10 September 2014|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141207151754/http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkManagement.aspx?id=N0102|archive-date=7 December 2014|df=dmy-all}}</ref> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| scope="row" rowspan="2" | '''Barrington Tops''' group;<br />north of [[Dungog, New South Wales|Dungog]] |
| scope="row" rowspan="2" | '''Barrington Tops''' group;<br />north of [[Dungog, New South Wales|Dungog]] |
||
| [[Barrington Tops National Park]] (part) |
| [[Barrington Tops National Park]] (part) |
||
| NSW |
| NSW |
||
| [[File:Barrington lookout.jpg|100px]] |
| [[File:Barrington lookout.jpg|100px]] |
||
| {{convert|765|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
| {{convert|765|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
||
| {{coord|32|3|10|S|151|29|37|E|display=inline}} |
| {{coord|32|3|10|S|151|29|37|E|display=inline}} |
||
|<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkManagement.aspx?id=N0002|title=Barrington Tops National Park|work=Office of Environment and Heritage|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|date=| |
|<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkManagement.aspx?id=N0002|title=Barrington Tops National Park|work=Office of Environment and Heritage|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|access-date=11 September 2014|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140911180235/http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkManagement.aspx?id=N0002|archive-date=11 September 2014|df=dmy-all}}</ref> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Mount Royal National Park]] (part) |
| [[Mount Royal National Park]] (part) |
||
| Line 598: | Line 629: | ||
| [[File:Mount Royal - eucalytus forest 2.jpg|100px]] |
| [[File:Mount Royal - eucalytus forest 2.jpg|100px]] |
||
| {{convert|69|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
| {{convert|69|km2|sqmi|disp=table}} |
||
| {{coord|32|12|1|S|151|19|25|E|display=inline}} |
| {{coord|32|12|1|S|151|19|25|E|display=inline}} |
||
|<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkManagement.aspx?id=N0107|title=Mount Royal National Park|work=Office of Environment and Heritage|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|date=| |
|<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkManagement.aspx?id=N0107|title=Mount Royal National Park|work=Office of Environment and Heritage|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|access-date=10 September 2014|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140911172223/http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/NationalParks/parkManagement.aspx?id=N0107|archive-date=11 September 2014|df=dmy-all}}</ref> |
||
|} |
|} |
||
| Line 612: | Line 643: | ||
==References== |
==References== |
||
{{reflist|30em}} |
{{reflist|30em}} |
||
=== Attribution === |
|||
{{NSW-SHR-CC-contains|name=Gondwana Rainforests of Australia|dno=5014148|id=01002|year=2018|access-date=2 June 2018}} |
|||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
* [http://environment.gov.au/heritage/places/world/gondwana/index.html World heritage listing for Gondwana Rainforests of Australia] |
* [http://environment.gov.au/heritage/places/world/gondwana/index.html World heritage listing for Gondwana Rainforests of Australia] |
||
* [http://www.bigvolcano.com.au/natural/whin.htm Introduction to Gondwana Rainforests of Australia] |
* [http://www.bigvolcano.com.au/natural/whin.htm Introduction to Gondwana Rainforests of Australia] |
||
* {{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/resources/parks/cerra-values-report.pdf|type=PDF|title=World Heritage and Associative Natural Values of the Central Eastern Rainforest Reserves of Australia|work=[[National Parks and Wildlife Service (New South Wales)|NSW National Parks & Wildlife Service]]|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]| |
* {{cite web|url=http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/resources/parks/cerra-values-report.pdf|type=PDF|title=World Heritage and Associative Natural Values of the Central Eastern Rainforest Reserves of Australia|work=[[National Parks and Wildlife Service (New South Wales)|NSW National Parks & Wildlife Service]]|publisher=[[Government of New South Wales]]|orig-year=June 2003 |date=December 2004|author=Hunter, R. John|ref=none}} |
||
{{World Heritage Sites in Australia}} |
{{World Heritage Sites in Australia}} |
||
[[Category:World Heritage Sites in New South Wales]] |
|||
{{coord|28.250|S|150.050|E|display=title|source:eswiki}} |
|||
[[Category:World Heritage Sites in Queensland]] |
|||
[[Category:World Heritage Sites in Australia]] |
|||
[[Category:Protected areas of Queensland]] |
[[Category:Protected areas of Queensland]] |
||
[[Category:Protected areas of New South Wales]] |
[[Category:Protected areas of New South Wales]] |
||
[[Category:Tourist attractions in Queensland]] |
[[Category:Tourist attractions in Queensland]] |
||
[[Category:Tourist attractions in New South Wales]] |
|||
[[Category:Australian National Heritage List]] |
[[Category:Australian National Heritage List]] |
||
[[Category:Gondwana Rainforests of Australia|*]] |
[[Category:Gondwana Rainforests of Australia|*]] |
||
| Line 634: | Line 666: | ||
[[Category:Protected areas established in 1986]] |
[[Category:Protected areas established in 1986]] |
||
[[Category:1986 establishments in Australia]] |
[[Category:1986 establishments in Australia]] |
||
[[Category:New South Wales State Heritage Register]] |
|||
[[Category:Articles incorporating text from the New South Wales State Heritage Register]] |
|||
[[Category:Eastern Australian temperate forests]] |
|||
[[Category:Subtropical rainforests]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 01:13, 13 February 2024
| UNESCO World Heritage Site | |
|---|---|
 Box Log Falls, Lamington National Park in Queensland | |
| Location | New South Wales and Queensland, Australia |
| Criteria | Natural: (viii), (ix), (x) |
| Reference | 368bis |
| Inscription | 1986 (10th Session) |
| Extensions | 1994 |
| Area | 370,000 ha (1,400 sq mi) |
| Coordinates | 28°15′S 150°3′E / 28.250°S 150.050°E |
From the Main Range in the north to the Barrington Tops in the south, various grouping of the Gondwana Rainforests on the Australian continent | |
| Official name | Gondwana Rainforests of Australia |
| Type | National heritage (landscape) |
| Designated | 17 December 1994 |
| Reference no. | 105135 |
| Class | Natural |
| Legal Status | Declared property |
| Official name | Gondwana Rainforests of Australia; Central Eastern Rainforest Reserves; Gondwana Rainforests of Australia (new name from 2007); North East Rainforests World Heritage Area |
| Type | State heritage (landscape) |
| Designated | 2 April 1999 |
| Reference no. | 1002 |
| Type | Wilderness |
| Category | Landscape – Natural |
The Gondwana Rainforests of Australia, formerly known as the Central Eastern Rainforest Reserves, are the most extensive area of subtropical rainforest in the world.[1] Collectively, the rainforests are a World Heritage Site with fifty separate reserves totalling 366,500 hectares (906,000 acres) from Newcastle to Brisbane.[2]
Background[edit]
The Gondwana Rainforests are so-named because the fossil record indicates that when Gondwana existed it was covered by rainforests containing the same kinds of species that are living today. Not all Gondwanan rainforests in Australia are located in the New South Wales – Queensland region; the largest Gondwanan rainforest in Australia is located in Tasmania's Tarkine wilderness. The number of visitors to the Gondwana rainforest reserves in New South Wales and Queensland is about 2 million per year.[1]
The World Heritage status of the region was created and negotiated initially in 1986, with the area extended in 1994, following a nomination which was prepared in 1992 by the Rainforest Conservation Society.[3] The World Heritage listing carries the following inscription:[1]
The Gondwana Rainforests of Australia is a serial property comprising the major remaining areas of rainforest in southeast Queensland and northeast New South Wales. It represents outstanding examples of major stages of the Earth’s evolutionary history, ongoing geological and biological processes, and exceptional biological diversity. A wide range of plant and animal lineages and communities with ancient origins in Gondwana, many of which are restricted largely or entirely to the Gondwana Rainforests, survive in this collection of reserves. The Gondwana Rainforests also provides the principal habitat for many threatened species of plants and animals.
— Brief synthesis of the Gondwana Rainforests of Australia as inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List.
The site was gazetted on the Australian National Heritage List on 21 May 2007[4] under the Environment and Heritage Legislation Amendment Act (No. 1), 2003 (Cth);[5] and the New South Wales portion was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 2 April 1999.[6]
Conservation value[edit]
The forests were inscribed to the World Heritage list in 1986, covering only the New South Wales sites of approximately 310,800 hectares (768,000 acres) and extended in 1994 to cover the Queensland sites of approximately 59,200 hectares (146,000 acres) which is a total of approximately 370,000 hectares (910,000 acres). The rainforest reserves have an extremely high conservation value, with more than 200 rare or threatened plant and animal species.[2]
Eight separate areas have been identified as having outstanding heritage significance to Australia and are included on the Australian National Heritage List.[4] The altitude of the reserves ranges from sea level to almost 1,600 m (5,200 ft).[7]
On 22 December 2000, the High Conservation Value Old Growth forest covering 24 national parks and 19 nature reserves spread across 12 local government areas in the upper north east region of New South Wales were listed on the New South Wales State Heritage Register.[8]
National parks[edit]
The Queensland areas include the Main Range, at its most northern point; and extending south, the Lamington, Mount Chinghee, Springbrook and Mount Barney national parks.
The New South Wales areas include the Barrington Tops, at its most southern point; and extending north, the Dorrigo, Mount Warning, New England, Mebbin, Nightcap, Border Ranges, Oxley Wild Rivers, Washpool, Willi Willi and Werrikimbe national parks.[9]
The most heavily visited parts are Dorrigo National Park and the Natural Bridge section of Springbrook National Park.[7]
Destruction[edit]
The region was historically logged extremely heavily, to such an extent that only 1% of the original range of the Gondwana rainforest remains in Australia. Most of the logged regions have been taken over by eucalyptus forest. [10]
During the 2019-2020 Australian bushfire season, many regions of the Gondwana rainforest were devastated by bushfires for the first time, with some preliminary reports indicating that up to 53% of the forests may have burned as of January 2020. Among the devastated habitats are several locations that are significant for some critically imperiled species, such as the nightcap oak and the giant barred frog. The presence of these devastating blazes in areas that have never burned before has been linked to the encroachment of the flammable eucalyptus trees into the logged areas adjoining the forests.[10][11] The general claim of "never burned before" has been challenged by several commentators, based on an article in The Cairns Post on 25 October 1951 that reported a "fire has burnt out about 2000 acres of thick rainforest country" in the Lamington National Park.[12]
Australian National Heritage List sections[edit]
The Gondwana Rainforests of Australia are divided into sections for listing on the Australian National Heritage List, from north to south, as below:
See also[edit]
- Environment of Australia
- Forests of Australia
- List of World Heritage Sites in Australia
- Mount Banda Banda
- Rainforest Way, a tourist drive featuring the Gondwana rainforests of south-eastern Queensland and north-eastern New South Wales
References[edit]
- ^ a b c "Gondwana Rainforests of Australia". Department of the Environment. Australian Government. Archived from the original on 26 July 2008. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ a b Reid, Greg (2004). Australia's National and Marine Parks: Queensland. South Yarra, Victoria: Macmillan Education Australia. p. 11. ISBN 0-7329-9053-X.
- ^ Keto, Aila; Scott, Keith (1992), The central eastern rainforests of Australia : World Heritage nomination, Rainforest Conservation Society, archived from the original on 27 October 2021, retrieved 14 October 2021
- ^ a b "Gondwana Rainforests of Australia, Lismore, NSW, Australia". Australian Heritage Database: Department of the Environment. Australian Government. 2014. Archived from the original on 10 May 2014. Retrieved 7 September 2014.
- ^ "Determination regarding including World Heritage places in the National Heritage List" (PDF). Special government gazette (PDF). Department of the Environment and Water Resources, Commonwealth of Australia. 21 May 2007. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 September 2014. Retrieved 30 August 2014.
- ^ "Gondwana Rainforests of Australia". New South Wales State Heritage Register. Department of Planning & Environment. H01002. Retrieved 2 June 2018.
Text is licensed by State of New South Wales (Department of Planning and Environment) under CC-BY 4.0 licence.
- ^ a b McGinley, Mark (9 December 2008). "Central Eastern Rainforest Reserves, Australia". Encyclopedia of Earth. United Nations Environment Programme: World Conservation Monitoring Centre. Archived from the original on 16 October 2009. Retrieved 1 July 2009.
- ^ "High Conservation Value Old Growth forest". New South Wales State Heritage Register. Department of Planning & Environment. H01487. Retrieved 18 May 2018.
Text is licensed by State of New South Wales (Department of Planning and Environment) under CC-BY 4.0 licence.
- ^ "Gondwana Rainforests of Australia". World Heritage List. UNESCO. Archived from the original on 27 May 2008. Retrieved 9 June 2008.
- ^ a b Shoebridge, Joanne; Marciniak, Catherine (18 January 2020). "Gondwana-era nightcap oak devastated by unprecedented bushfire". ABC News (Australia). Archived from the original on 18 January 2020. Retrieved 18 January 2020.
- ^ Cox, Lisa; Evershed, Nick (16 January 2020). "'It's heart-wrenching': 80% of Blue Mountains and 50% of Gondwana rainforests burn in bushfires". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 18 January 2020. Retrieved 18 January 2020.
- ^ "Bushfires Over Large Part of State". The Cairns Post. 25 October 1951. p. 1 – via Trove.
- ^ a b "Main Range National Park and Spicers Gap Road Regional Park Management Statement 2013". Department of National Parks, Recreation, Sport and Racing. Government of Queensland. 11 November 2013. Archived from the original on 8 September 2014. Retrieved 7 September 2014.
- ^ a b Hunter, R. John (December 2004) [June 2003]. "9.2 Main Range Group". World Heritage and Associative Natural Values of the Central Eastern Rainforest Reserves of Australia (PDF). Government of New South Wales. p. 66. Archived (PDF) from the original on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 22 September 2014.
- ^ "Mallanganee National Park". Office of Environment and Heritage. Government of New South Wales. Archived from the original on 7 September 2014. Retrieved 7 September 2014.
- ^ "Mount Clunie National Park". Office of Environment and Heritage. Government of New South Wales. Archived from the original on 11 September 2014. Retrieved 10 September 2014.
- ^ "Mount Nothofagus National Park". Office of Environment and Heritage. Government of New South Wales. Archived from the original on 11 September 2014. Retrieved 10 September 2014.
- ^ "Tooloom National Park: Park management". Office of Environment and Heritage. Government of New South Wales. Archived from the original on 10 September 2014. Retrieved 10 September 2014.
- ^ "Toonumbar National Park". Office of Environment and Heritage. Government of New South Wales. Archived from the original on 11 September 2014. Retrieved 10 September 2014.
- ^ "Border Ranges National Park: Park management". NSW National Parks & Wildlife Service. Government of New South Wales. Archived from the original on 11 September 2014.
- ^ "Limpinwood Nature Reserve: Park management". Office of Environment and Heritage. Government of New South Wales. Archived from the original on 5 December 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- ^ "Numinbah Nature Reserve: Park management". Office of Environment and Heritage. Government of New South Wales. Archived from the original on 13 September 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- ^ "Springbrook National Park: Nature, culture and history". Department of Environment, Resources, and Mining. Government of Queensland. 29 April 2009. Archived from the original on 24 March 2010. Retrieved 12 July 2009.
- ^ "Wollumbin National Park". NSW National Parks & Wildlife Service. Government of New South Wales. 24 September 2013. Archived from the original on 2 May 2014. Retrieved 1 May 2014.
- ^ "Iluka Nature Reserve: Park management". Office of Environment and Heritage. Government of New South Wales. Archived from the original on 11 October 2014. Retrieved 23 September 2014.
- ^ "Mount Hyland Nature Reserve: Park management". Office of Environment and Heritage. Government of New South Wales. Archived from the original on 5 December 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- ^ "New England National Park: Park management". Office of Environment and Heritage. Government of New South Wales. Archived from the original on 11 September 2014. Retrieved 10 September 2014.
- ^ "Oxley Wild Rivers National Park: Park Management". Office of Environment and Heritage. Government of New South Wales. Archived from the original on 11 September 2014. Retrieved 10 September 2014.
- ^ "The Castles Flora Reserve (NSW)". Gazetteer of Australia online. Geoscience Australia, Australian Government.
- ^ "Werrikimbe National Park". Office of Environment and Heritage. Government of New South Wales. Archived from the original on 12 September 2014. Retrieved 10 September 2014.
- ^ "Willi Willi National Park". Office of Environment and Heritage. Government of New South Wales. Archived from the original on 7 December 2014. Retrieved 10 September 2014.
- ^ "Barrington Tops National Park". Office of Environment and Heritage. Government of New South Wales. Archived from the original on 11 September 2014. Retrieved 11 September 2014.
- ^ "Mount Royal National Park". Office of Environment and Heritage. Government of New South Wales. Archived from the original on 11 September 2014. Retrieved 10 September 2014.
Attribution[edit]
This Wikipedia article contains material from Gondwana Rainforests of Australia, entry number 01002 in the New South Wales State Heritage Register published by the State of New South Wales (Department of Planning and Environment) 2018 under CC-BY 4.0 licence, accessed on 2 June 2018.
External links[edit]
- World heritage listing for Gondwana Rainforests of Australia
- Introduction to Gondwana Rainforests of Australia
- Hunter, R. John (December 2004) [June 2003]. "World Heritage and Associative Natural Values of the Central Eastern Rainforest Reserves of Australia" (PDF). NSW National Parks & Wildlife Service (PDF). Government of New South Wales.
- World Heritage Sites in New South Wales
- World Heritage Sites in Queensland
- Protected areas of Queensland
- Protected areas of New South Wales
- Tourist attractions in Queensland
- Australian National Heritage List
- Gondwana Rainforests of Australia
- Forests of New South Wales
- Forests of Queensland
- Great Dividing Range
- Protected areas established in 1986
- 1986 establishments in Australia
- New South Wales State Heritage Register
- Eastern Australian temperate forests
- Subtropical rainforests